담당자정보
- 부서 : 투자유치부
- 문의전화 : 043-220-8372
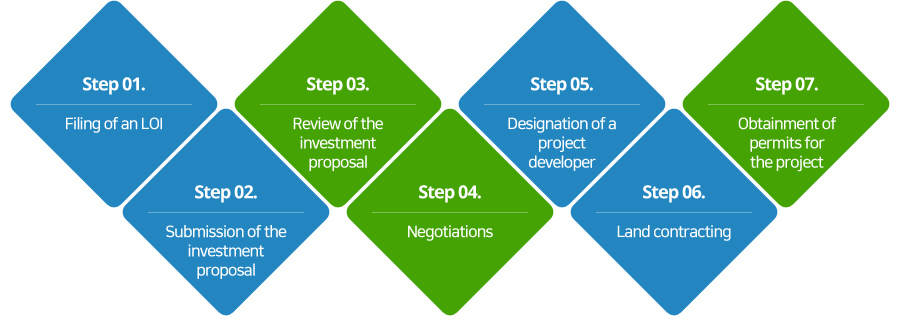
Investment procedure

| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|

| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|

| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|

| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|

| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|
| Description | Supports |
|---|---|
|
|
Investment programs
Foreigner (Art. 2 of the Foreign Investment Promotion Act; Art. 2 of the Enforcement Decree of the FIPA)
- Any individual of foreign nationality
- Any legal entity incorporated under the laws of a foreign country (foreign corporation)
- Any international cooperative organization
- Any agency offering international economic cooperation for and on behalf of a foreign government
- The IBRD, the IFC, the ADB or any other international organization performing development financial services
- Any international organization performing international investment services for itself or any other entity
- Any Korean national who is granted permanent residency in another country
Types of foreign investment (Art. 2 (4) of the FIPA; Art. 2 (2) of the Enforcement Decree of the FIPA)
- Where a foreigner acquires shares and/or equity interests in domestic businesses
- Where a foreigner owns 10% or more of voting capital stock or the total voting equity investment
- Where a foreigner owning less than 10% or more of voting capital stock or the total voting equity investment enters into any contract:
- that allows the foreigner to dispatch or elect officers
- under which raw materials or products are delivered or purchased for a period of one year or more or
- under which technology is provided, introduced or jointly researched and developed.
- Major facilities: medical tourism facilities, tourist resort facilities, and educational research and development facilities
- The amount of investment (per person if two or more foreigners are included in the investors) is 100 million Korean won or more.
Long-term loans
- The overseas parent of a foreign-invested company
- Any five-year or longer loan that is extended to a foreign-invested company by any of the following companies holding an equity interest in the overseas parent of such foreign-invested company:
- any overseas company holding a 50% or more equity interest in such overseas parent; or
- where an overseas parent holds a 50% or more equity interest in such foreign-invested company:
- any overseas company holding a 10% or more equity interest in such overseas parent;
- any overseas company in which such overseas parent holds a 50% or more equity interest; or
- any overseas company holding a 50% or more equity interest in any other overseas company that holds a 50% or more equity interest in such overseas parent.